MongoDB
MongoDB is a:
- Flexible
- Scalable (scale-out)
- General-purpose
- Document-Oriented database
Features of MongoDB:
Indexing: MongoDB supports generic secondary indexes and provides unique, compound, geospatial, and full-text indexing capabilities as well. Secondary indexes on hierarchical structures such as nested documents and arrays are also supported and enable developers to take full advantage of the ability to model in ways that best suit their applications
Aggregation: MongoDB provides an aggregation framework based on the concept of data processing pipelines. Aggregation pipelines allow you to build complex analytics engines by processing data through a series of relatively simple stages on the server side, taking full advantage of database optimizations
Special collection and index types: MongoDB supports time-to-live (TTL) collections for data that should expire at a certain time, such as sessions and fixed-size (capped) collections, for holding recent data, such as logs. MongoDB also supports partial indexes limited to only those documents matching a criteria filter in order to increase efficiency and reduce the amount of storage space required
File Storage: MongoDB supports an easy-to-use protocol for storing large files and file metadata
Applications send query for data to MongoDB Server. MongoDB Server gets the data through a Storage Engine, which handles the actual reading and writing of the data to the database
Setup
Installation steps for both (L)UNIX and Windows systems
Linux Setup
Install MongoDB using your favourite package manager for your distro or build one for your system
After installation, configure MongoDB.
mongod(MongoDB Demon) will be used for configuration:bash# create directory for database storage sudo mkdir -p /data/db sudo chown -Rv $(whoami) /data/dbStart the mongo server:
mongodOpen a new terminal and start working on MongoDB:
mongoEvery time we want to work on MongoDB. We need to start the
mongodevery time. So, we have to add MongoDB as a service, this will start the MongoDB service every time system boots upOptionally provide database and log path:
bashmongod --dbpath /data/db --logpath /data/logs/.mongorc.jsLoads whenever the shell is started
Windows Setup
Download and install MongoDB from MongoDB Site, use the default settings (customize the paths is you need to)
Add the MongoDB installed path to your Environment variable Path (change the version number accordingly i.e. 4.2 to the installed version)
C:\Program Files\MongoDB\Server\4.2\bin\Open command prompt and run
mongoto start the MongoDB shell to interact with the DB
Other applications required are:
- Install Robo 3T (Robomongo), a GUI to interact with the MongoDB database. It's an alternative to MongoDB Compass
Databases, Collections, And Documents
A document is the basic unit of data for MongoDB and is roughly equivalent to a row in a relational database management system (but much more expressive)
A collection can be thought of as a table with a dynamic schema that contains documents
A single instance of MongoDB can host multiple independent databases, each of which contains its own collections
Databases and Collections are created "lazily" or implicitly (when a Document is inserted)
Documents
Document is an ordered set of keys with associated values
A value can be one of several different Data Types supported by MongoDB
Every document has a special key,
_id, that is unique within a collection. By default a unique_idis generated if explicitly not providedDocuments can have embedded documents and array fields
MongoDB is type-sensitive and case-sensitive
javascript// THE BELOW DOCUMENTS ARE DIFFERENT FROM EACH OTHER // TYPE-SENSITIVITY OF VALUE, NUMBER VS STRING {"count" : 5} {"count" : "5"} // CASE-SENSITIVITY OF KEY {"count" : 5} {"Count" : 5}
Keys
Keys can be any UTF-8 character, with some exceptions:
- Keys must not contain the character \0 (the
nullcharacter). This character is used to signify the end of a key - The
.and$characters are reserved characters - All the keys inside a document must be unique to that document
Embedded Documents:
- Up to 100 Levels of Nesting
- Maximum size of each documents is 16 MB.
Collections
A collection is a group of documents
Collection names can be any UTF-8 string, with few restrictions:
The empty string ("") is not valid
Collection names may not contain the character \0 (the
nullcharacter), because this delineates the end of a collection namesystem should not be used as it is a reserved for internal collections
Also
$and.is a reserved word and should not be used in the collection namesCollections can be organized using namespace sub-collections separated by the
.character
Commands:
show collections: List of collectionsdb.collectionName.insertOne({.}): Creates a collection if not present and inserts one documentdb.<collectionName>.find().pretty(): List of all documents present in the collectiondb.<collectionName>.drop()
Databases
MongoDB groups collections into databases
- Database names:
The empty string ("") is not valid
Special characters such as
/,*,.,"*,**,<,>,:,|,?,$, (a single space), or\0(thenullcharacter) should not be used in database namesDatabase names are case-insensitive
Database names are limited to a maximum of 64 bytes
Commands:
show dbs: List of databasesuse newDBName: Creates a new databasedb: To check which database is in usedb.createUser({ ... }): Create user for the database
Some reserved database names:
admin: The admin database plays a role in authentication and authorizationlocal: This database stores data specific to a single server. In replica sets, local stores data used in the replication process. The local database itself is never replicatedconfig: Sharded MongoDB clusters use the config database to store information about each shard
Data Types
String: Any strings of UTF-8 and must be enclosed in double or single quotes
Boolean:
trueandfalse.Number: By default all numeric values are stored as (in mongo shell) 64-bit floating-point numbers, which have much less precision than decimal numbers
- Integer (int32):
55written usingNumberInt(55). - NumberLong (int64):
10000000000 - NumberDecimal Doubles (64bit):
12.99 - High Precision Doubles (128bit):
- Integer (int32):
ObjectID: Unique 12-byte IDs (temporal component) -
ObjectID("UUID").Date: Stores dates in ISO format -
ISODate("2018-09-09")and{"today" : new Date()}.- Timestamp: It is a special type for internal MongoDB use and not directly associated with the regular Date type
Embedded Documents: Documents can contain entire documents embedded as values in a parent document:
Array: A collection of items
Null: A key with value as
nullor a non-existent valueRegular Expression: Values can be JavaScript's regular expression syntax -
{"regex" : /foobar/i}.Binary Data: Binary data is a string of arbitrary bytes. It cannot be manipulated from the shell. Binary data is the only way to save non-UTF-8 strings to the database
Code: MongoDB also makes it possible to store arbitrary JavaScript in queries and documents -
{"x" : function() { /* ... */ }}.
Operations
CRUD Operations
find()returns a cursor, not a list of documents- Filters and operators (
$gt...) can be used to retrieve specify particular documents and also limit the number of documents
CREATE Documents
insertOne(): Insert one document at a time with or without user defined_id.javascript// UNIQUE ID GIVEN BY MongoDB db.collectionName.insertOne({key: "value"}) // UNIQUE ID GIVEN BY THE USER db.collectionName.insertOne({_id: "4984" key: "value"})insertMany(): Insert multiple documents by passing an array of documentsjavascriptdb.collectionName.insertMany([{ key: "value" }, { key: "value" }]);MongoDB dose not accept message longer than 48MB and will split into batches of 48MB if message is large
insert(): Insert one or more documents at a time. It is not recommended to use. Also, this command dose not return the ID of the inserted documentjavascriptdb.collectionName.insert();mongoimport: Import documents from an external filebashmongoimport -d cars -c carsList --drop --jsonArray
Insert Options:
Ordered Insert: MongoDB by default inserts documents in a Ordered Insert method i.e. While inserting multiple documents, each document is processed and inserted separately. If one of the document insertion fails, MongoDB stops insertion of rest of the documents. All the documents before the error were inserted
MongoDB will not rollback documents inserted before the error
Ordered insert can be disabled, so that the documents after the error are also inserted
javascriptdb.collectionName.insertMany( [ { _id: "yoga", name: "Yoga" }, { _id: "yoga", name: "Yoga" }, { _id: "Cooking", name: "Cooking" }, ], { ordered: false } ); // IN THIS EXAMPLE DOCUMENT WITH _id: "Cooking" WILL BE INSERTED EVEN THOUGH THERE WAS AN ERROR IN THE PREVIOUS DOCUMENT
Write Concern: Write concern describes the level of acknowledgment requested from MongoDB for write operations
Here,
w: 1is acknowledgment is requested on a write operation and it isw: 0if no acknowledgment is needed. Ifwis greater than 1 then it requires acknowledgment from the primary and as many data-bearing secondaries as needed to meet the specified write concern. Specifyingw: 2would require acknowledgment from the primary and one of the secondaries. Specifyingw: 3would require acknowledgment from the primary and both secondariesThe
joption requests acknowledgment from MongoDB that the write operation has been written to the on-disk journal.This option specifies a time limit, in milliseconds, for the write concern.
wtimeoutis only applicable forwvalues greater than1.wtimeoutcauses write operations to return with an error after the specified limit, even if the required write concern will eventually succeed. When these write operations return, MongoDB does not undo successful data modifications performed before the write concern exceeded thewtimeouttime limit. If you do not specify thewtimeoutoption and the level of write concern is unachievable, the write operation will block indefinitely. Specifying awtimeoutvalue of0is equivalent to a write concern without thewtimeoutoptionjavascriptdb.collectionName.insertOne({_id: "yoga", name: "Yoga"}, { w: <value>, j: <boolean>, wtimeout: <number> });
Atomicity: If an operation fails on a document, then the operation will be rolled back for only that document. The document is either saved or not saved
Import Documents from JSON File
mongoimport JSONFileName.json -d dataBaseName -c collectionName --jsonArray --drop
READ Documents
Operators
- Query Operator: Used to locate the data. Example -
$eq. - Projection Operator: Used to modify the data presentation. Example -
$. - Update operator: Used to modify/add additional data. Example -
$inc.
DELETE Documents
deleteOne(): Deletes the first document that matches the filter. It takes a filter document as first parameter. This filter specifies a set of criteria to match against a document that needs to be removeddeleteMany(): Similar todeleteOne(), this deletes many documents at a timedeleteMany({})will remove all the documents in a collection
removeis still supported but should not be used
DROP
- Select the database:
use databaseName. - Drop the database:
db.dropDatabase(). - Similarly, to drop a collection use:
db.collectionName.drop().
UPDATE Documents
updateOne(): Updates one document. Takes a filter document as the first parameter and a modifier document, which describes changes to make, as the second parameterupdateMany(): Updates many documents. Parameters are same as inupdateOne().- Updating a document is atomic: if two updates happen at the same time, whichever one reaches the server first will be applied, and then the next one will be applied
Expect value of
_idevery other value can be modified
Update Operators:
$set: Sets the value of a field. If the field dose not yet exist, it will be created$unset: Removes the required field$inc: Increments the value of type integer, long, decimal, or decimal. It will create the field if not already present. It is used as the second parameter to update operations.db.movies.updateOne({'title': 'Matrix'}, {'$inc': {'rating': 1}})$rename: Rename a field.db.collection.updateMany({}, {$rename: {oldFieldName: "newFieldName"}}).
Array Operations
$push: Adds elements to the end of an array if the array exists and creates a new array if it does notIf you want to add or append an array, use
$each.db.movies.updateOne({"genre" : "horror"}, {"$push" : {"hourly" : {"$each" : [562.776, 562.790, 559.123]}}})If you want to limit the size of an array, use
$slice. It will replace old values to fit the new ones.db.movies.updateOne({"genre" : "horror"}, {"$push" : {"top10" : {"$each" : ["Nightmare on Elm Street", "Saw"], "$slice" : -10}}}).If you want to sort the values inside an array before slicing them, use
$sort.To prevent insertion of duplicate values we can use
$ne(not-equal-to) operator.db.movies.updateOne({"titles" : {"$ne": "Jaws"}, {$push: {"titles": "Jaws"}}},To prevent duplicates and treat an array as a set, use
$addToSet. The$eachoperator can be used along with this operator, not with$neoperatorjavascriptdb.movies.updateOne({ name: 1 }, { $addToSet: { genre: "Comedy" } }); // ALONG WITH "$each" db.movies.updateOne( { name: 1 }, { $addToSet: { genre: { $each: ["Comedy", "Drama", "Horror"] } } } );
$pop: Remove elements from an array,{"$pop": {"key": 1}}: Removes an element from the end of an array{"$pop": {"key": -1}}: Removes an element from the beginning
Updates on an array element can be done through:
The index value of the element. MongoDB uses 0-based indexing. We can directly reference the required element in an array.
db.tv.findOne({"genres.2": "Family"}).If the index of an element is unknown, then the position operator
$can be used.db.tv.findOne({"reviews.$.author": "Jim"}).To update all the elements in an arrary, use
$[]javascriptdb.blog.updateOne( {"post" : post_id }, { $set: { "comments.$[].hidden" : true } }, } )
Array filtering using
arrayFilters:javascriptdb.blog.updateOne( { post: post_id }, { $set: { "comments.$[elem].hidden": true } }, { arrayFilters: [{ "elem.votes": { $lte: -5 } }], } );This command defines
elemas the identifier for each matching element in the"comments"array. If thevotesvalue for the comment identified byelemis less than or equal to-5, we will add a field called"hidden"to the"comments"document and set its value totrue.
$eachneeds to used before using any of the array operators
Document Replacement
replaceOne(): Replace a document fully with a new one. Takes a filter as the first parameter, but as the second parameter it expects a document with which it will replace the document matching the filter
Joining Documents
$lookup is used to join two documents
// CUSTOMERS DOCUMENT
{
uerName: 'ABD',
favBooks: ['id1', 'id2']
}// BOOKS
{
_id: 'id1',
name: 'Lord of the Rings'
}customers.aggregate([
{
$lookup: {
from: "books",
localField: "favBooks",
foreignField: "_id",
as: "favBookData",
},
},
]);Schema
MongoDB supports dynamic schemas (dose not enforces any schema), i.e. documents don't have to use the same schema inside of one collection
Schema Validation
- Validation Level:
- Which documents get validated?
- strict: All inserts and updates are validated
- moderate: All inserts and updates to correct documents are validated
- Validation Action:
- What happens if validation fails?
- error: Throw error and don't insert or update the document
- warn: Log warning but proceed with the operation
Adding Validation:
db.createCollection("posts", {
validator: {
$jsonSchema: {
bsonType: "object",
required: ["title", "text", "creator", "comments"],
properties: {
title: {
bsonType: "string",
description: "must be a string and is required",
},
text: {
bsonType: "string",
description: "must be a string and is required",
},
creator: {
bsonType: "objectId",
description: "must be an objectid and is required",
},
comments: {
bsonType: "array",
description: "must be an array and is required",
items: {
bsonType: "object",
required: ["text", "author"],
properties: {
text: {
bsonType: "string",
description: "must be a string and is required",
},
author: {
bsonType: "objectId",
description: "must be an objectid and is required",
},
},
},
},
},
},
},
});Modify Validation Settings:
db.runCommand({
collMod: "posts",
validator: {
$jsonSchema: {
bsonType: "object",
required: ["title", "text", "creator", "comments"],
properties: {
title: {
bsonType: "string",
description: "must be a string and is required",
},
text: {
bsonType: "string",
description: "must be a string and is required",
},
creator: {
bsonType: "objectId",
description: "must be an objectid and is required",
},
comments: {
bsonType: "array",
description: "must be an array and is required",
items: {
bsonType: "object",
required: ["text", "author"],
properties: {
text: {
bsonType: "string",
description: "must be a string and is required",
},
author: {
bsonType: "objectId",
description: "must be an objectid and is required",
},
},
},
},
},
},
},
validationAction: "warn",
});Indexes
db.collectionName.createIndex({"dob.age": 1})
Geo-spatial Data
GeoJSON
Aggregation Framework
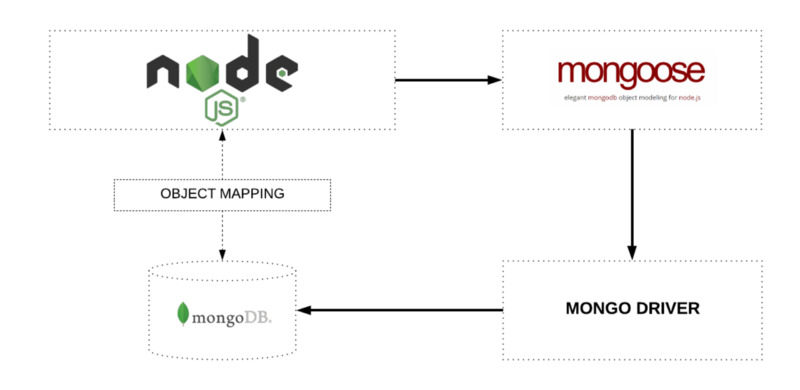
Mongoose
Mongoose is an Object Data Modelling (ODM) library for MongoDB and Node.js. It manages relationships between data, provides schema validation, and is used to translate between objects in code and the representation of those objects in MongoDB