VPC
- VPC is something you should know in depth for the AWS Certified Solutions Architect Associate & AWS Certified SysOps Administrator
- At the AWS Certified Developer Level, you should know about:
- VPC, Subnets, Internet Gateways & NAT Gateways
- Security Groups, Network ACL (NACL), VPC Flow Logs
- VPC Peering, VPC Endpoints
- Site to Site VPN & Direct Connect
- I will just give you an overview, less than1 or 2 questions at your exam
- Later in the course, I will be highlighting when VPC concepts are helpful
VPC & Subnets Primer
- VPC: private network to deploy your resources (regional resource)
- Subnets allow you to partition your network inside your VPC (Availability Zone resource)
- A public subnet is a subnet that is accessible from the internet
- A private subnet is a subnet that is not accessible from the internet
- To define access to the internet and between subnets, we use Route Tables
Internet Gateway & NAT Gateways
- Internet Gateways helps our VPC instances connect with the internet
- Public Subnets have a route to the internet gateway
- NAT Gateways (AWS-managed) & NAT Instances (self-managed) allow your instances in your Private Subnets to access the internet while remaining private
Network ACL & Security Groups
NACL (Network ACL)
- A firewall which controls traffic from and to subnet
- Can have ALLOW and DENY rules
- Are attached at the Subnet level
- Rules only include IP addresses
Security Groups
- Act as virtual firewall that controls traffic to and from an ENI / an EC2 Instance
- Can have only ALLOW rules
- Rules include IP addresses and other security groups
- Each instance can have up to 5 security groups
Network ACLs vs Security Groups
| Security Group | Network ACL |
|---|---|
| Operates at the instance level | Operates at the subnet level |
| Supports allow rules only | Supports allow rules and deny rules |
| Is stateful: Return traffic is automatically allowed, regardless of any rules | Is stateless: Return traffic must be explicitly allowed by rules |
| We evaluate all rules before deciding whether to allow traffic | We process rules in number order when deciding whether to allow traffic |
| Applies to an instance only if someone specifies the security group when launching the instance, or associates the security group with the instance later on | Automatically applies to all instances in the subnets it's associated with (therefore, you don't have to rely on users to specify the security group) |
VPC Flow Logs
- Capture information about IP traffic going into your interfaces:
- VPC Flow Logs
- Subnet Flow Logs
- Elastic Network Interface Flow Logs
- Helps to monitor & troubleshoot connectivity issues. Example:
- Subnets to internet
- Subnets to subnets
- Internet to subnets
- Captures network information from AWS managed interfaces too: Elastic Load Balancers, ElastiCache, RDS, Aurora, etc...
- VPC Flow logs data can go to S3 / CloudWatch Logs
VPC Peering
- Connect two VPC, privately using AWS' network
- Make them behave as if they were in the same network
- Must not have overlapping Classless Interdomain Routing (CIDR: uses variable length subnets masks (VLSM)) (IP address range)
- VPC Peering connection is not transitive (must be established for each VPC that need to communicate with one another)
VPC Endpoints
- Endpoints allow you to connect to AWS Services using a private network instead of the public www network
- This gives you enhanced security and lower latency to access AWS services
- VPC Endpoint Gateway: S3 & DynamoDB
- VPC Endpoint Interface: the rest
- Only used within your VPC
Site to Site VPN & Direct Connect
- Site to Site VPN
- Connect an on-premises VPN to AWS
- The connection is automatically encrypted
- Goes over the public internet
- Direct Connect (DX)
- Establish a physical connection between on-premises and AWS
- The connection is private, secure and fast
- Goes over a private network
- Takes at least a month to establish
- Note: Site-to-site VPN and Direct Connect cannot access VPC endpoints
VPC Closing Comments
VPC: Virtual Private Cloud
Subnets: Tied to an AZ, network partition of the VPC
Internet Gateway: at the VPC level, provide Internet Access
NAT Gateway / Instances: give internet access to private subnets
NACL: Stateless, subnet rules for inbound and outbound
Security Groups: Stateful, operate at the EC2 instance level or ENI
VPC Peering: Connect two VPC with non overlapping IP ranges, non transitive
VPC Endpoints: Provide private access to AWS Services within VPC
VPC Flow Logs: network traffic logs
Site to Site VPN: VPN over public internet between on-premises DC and AWS
Direct Connect: direct private connection to a AWS
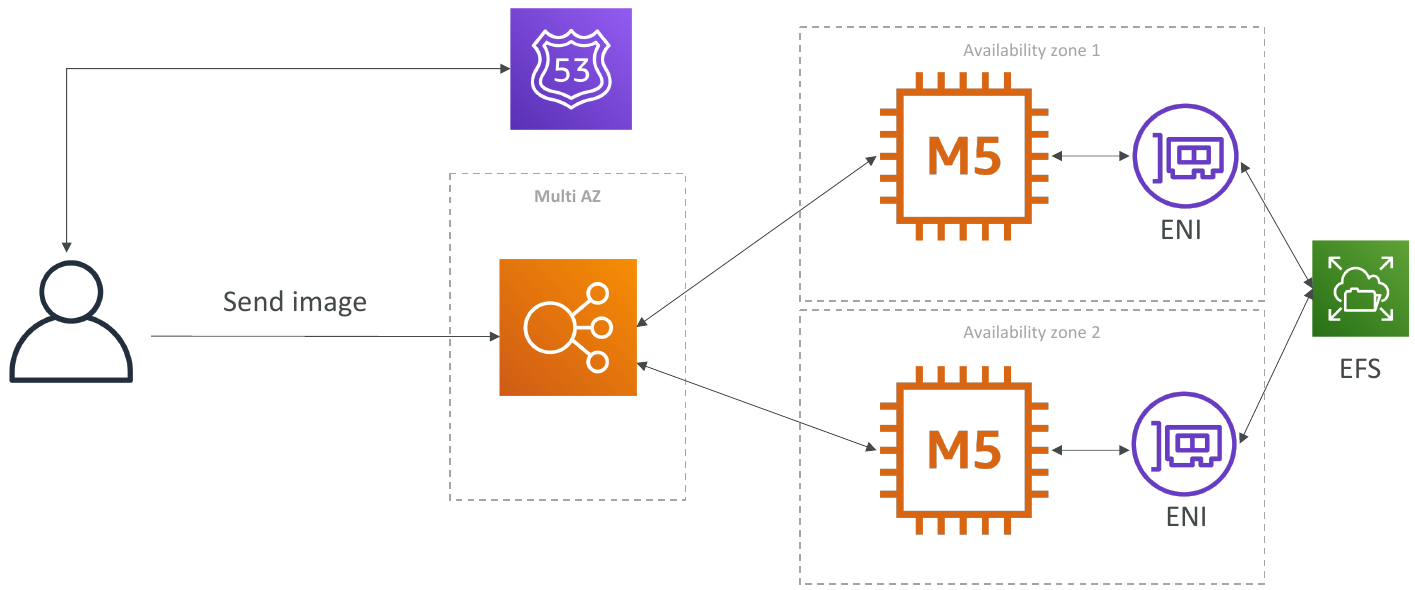
Typical Solution Architecture
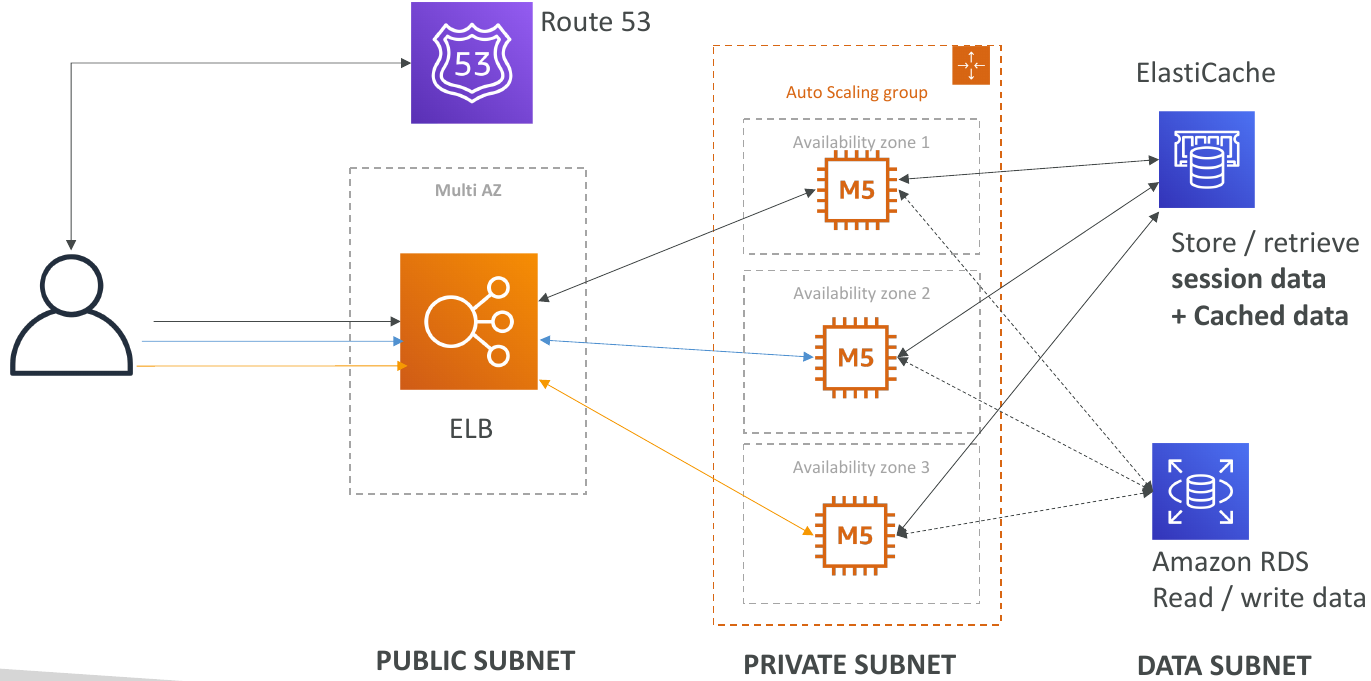
LAMP Stack on EC2
- Linux: OS for EC2 instances
- Apache: Web Server that run on Linux (EC2)
- MySQL: database on RDS
- PHP: Application logic (running on EC2)
- Can add Redis / Memcached (ElastiCache) to include a caching tech
- To store local application data & software: EBS drive (root)
Wordpress on AWS